When you think of welding, you may think of various industrial applications. Although laser welding technology has changed the manufacturing industry, its most significant impact is in the field that requires versatility, accuracy, and precision: medical laser welding. Medical laser welding is vital in improving medical devices’ and equipment’s quality and consistency while minimizing production costs.
What Laser Welding Is
It is a surprisingly delicate and precise welding technique that uses beam light to fuse parts of metal. A freestanding laser source produces this laser beam, which is directed to a hand-held collimator or machine-mounted ‘torch’ and onto the workpiece. According to experts at Micro Weld, this directed energy beam helps to heat and melt the workpiece, and the melt pool joins the targets together to form well-integrated welds.
How It Works
You can automate the laser welding process on various materials and fragile parts. Alloys and laser-welded metals include gold, copper, titanium, aluminum, and steel. When it comes to laser welding, external materials are not used. Therefore, the welding process is carried out by melting all the areas that should be welded. The energy supplied makes it possible to exceed or reach the material’s melting temperature.
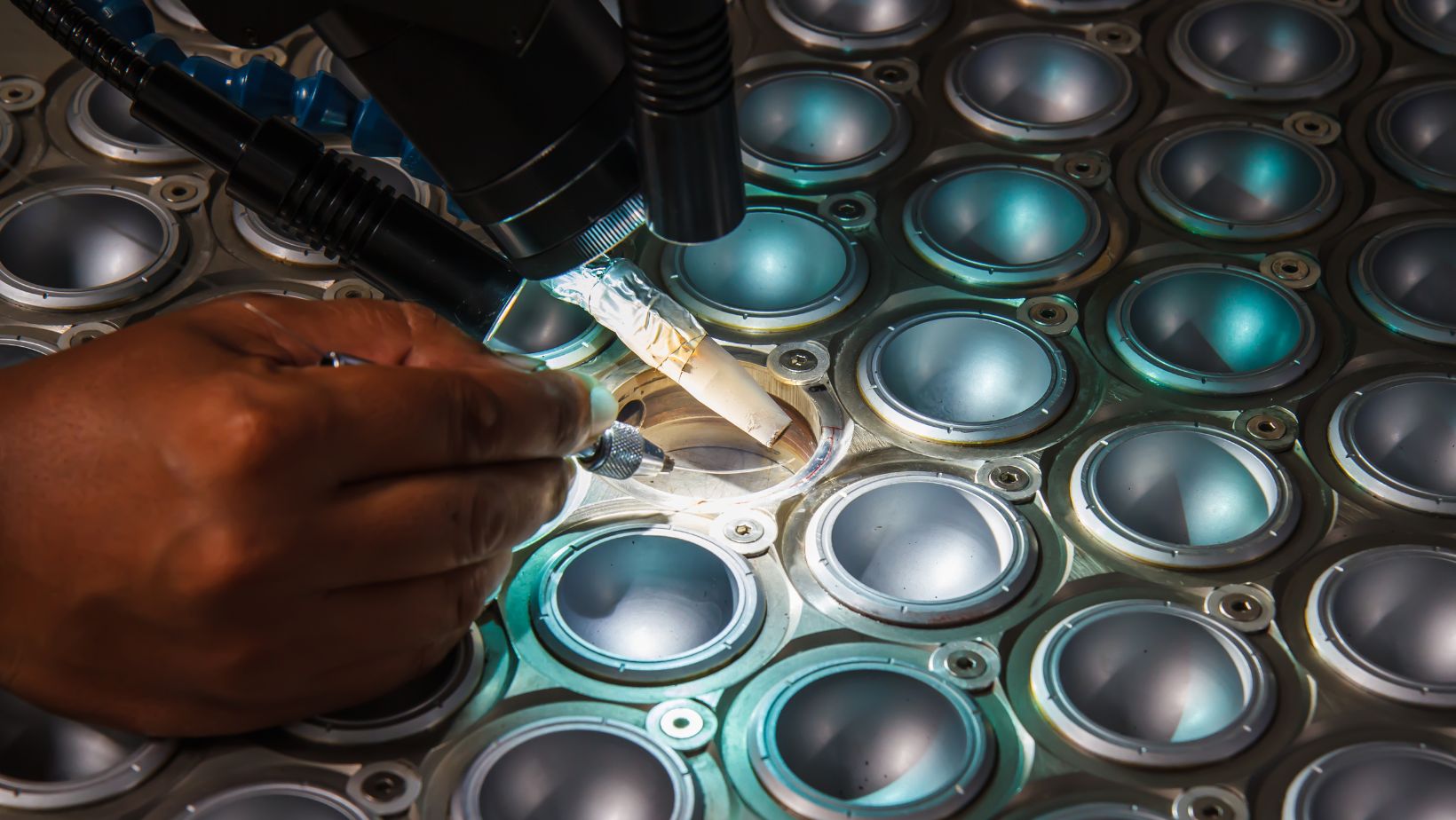
It is crucial to note that using an inert gas, like helium or argon, helps prevent oxygen bubbles from forming during the material’s liquid phase. This, in turn, minimizes the porosity during the process. You can easily control the laser beam width and penetration depth by using different kinds of focusing mirrors, like double-focus mirrors. So, we can conclude that laser technology allows for various geometries with continuous weld seams or spots.
Reasons for Using Laser Welding in the Medical Industry
Laser welding in the medical industry holds a couple of benefits. Some of the reasons the medical industry uses laser welding include the following:
- Flexibility and Speed
Laser welding is one of the fastest techniques. Based on the power and type of laser used, you can weld thinner sections of materials at a high speed of several meters per minute. Therefore, the laser is best suited to work in high-productivity and automated environments. For a thicker section, productivity gains can be made, too, as the keyhole welding procedure may complete a joint in just one pass that would otherwise need several passes with other methods.
- Low Input of Heat
Laser welding often transmits heat in controlled and small areas. Other methods, such as microscopic TIG welding and MIG welding, have significant inputs of heat that cause more stress on components. Controlling heated affected areas with laser welding techniques keeps metallurgical structures intact.
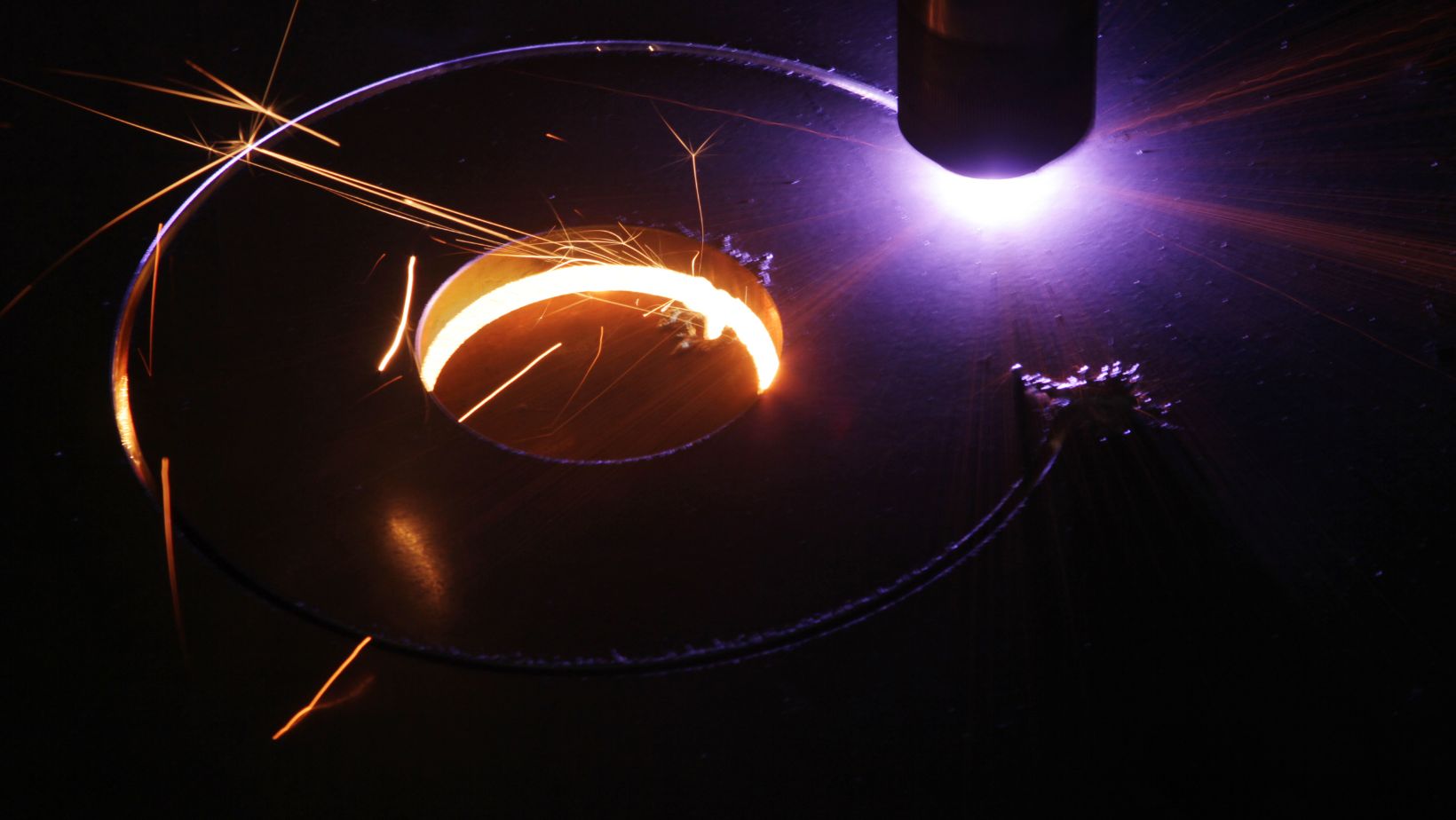
The outcome is high-quality welds, which require less heat treatment and finishing. In addition, controlled heat zones of the laser welding process make it possible for welders to weld devices’ exteriors without interfering with thermal-sensitive internal parts.
- High Precision
The medical industry prefers laser welding because the process can produce components with high precision, thanks to the beam focusing on small areas. It is also possible to control lasers to satisfy particular parameters, including the size of the beam, which ensures there is no material damage, distortion, or crack. The process also produces durable and strong welds that withstand extreme temperatures and harsh environments. Laser beams often have very narrow weld profiles, which enables welders to weld a thin workpiece without damaging it.
In conclusion, laser welding is indispensable in many sectors, including the medical industry. Thanks to the method’s high precision, speed, flexibility, and low heat input, the medical industry depends on it to create various devices, like catheters.

More Stories
What to Look for When Researching Ultimate Universities Abroad
What To Do When A Frozen Bank Account Disrupts Your Cash Flow
How Does The Electrical Resistivity Of Inconel 718 Change With Temperature